How To Tell If Data Is Symmetric
Descriptive Statistics > Symmetric Distribution
A symmetric distribution is a type of distribution where the left side of the distribution mirrors the right side. By definition, a symmetric distribution is never a skewed distribution. This should exist intuitive: try and describe lines of symmetry through a skewed distribution (you lot tin can't).
The normal distribution is symmetric. Information technology is also a unimodal distribution (it has 1 pinnacle).
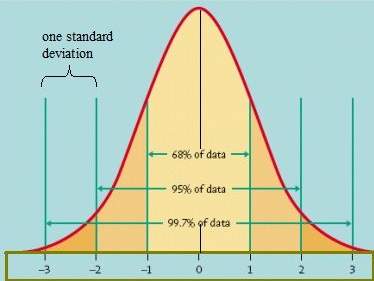
Standard normal distribution. Image credit: University of Virginia.
Distributions don't have to be unimodal to exist symmetric. They can be bimodal (2 peaks) or multimodal (many peaks). The following bimodal distribution is symmetric, as the 2 halves are mirror images of each other.
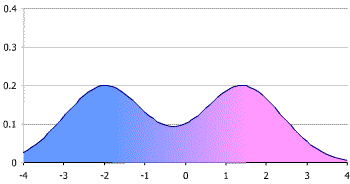
Mean, Mode and Median in a Symmetric Distribution
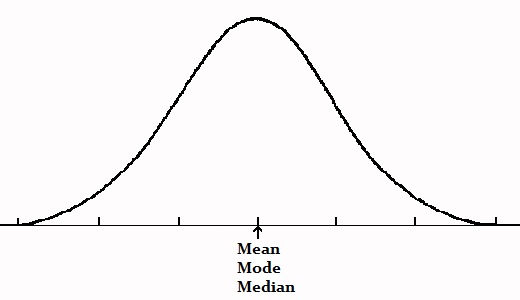
In a symmetric distribution, the mean, mode and median all fall at the same point. The style is the almost common number and it matches with the highest meridian (the "mode" here is unlike from the "mode" in bimodal or unimodal, which refers to the number of peaks).
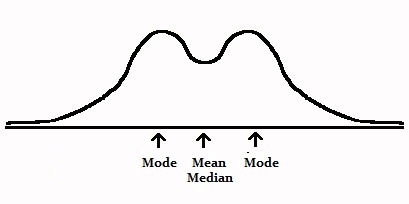
An exception is the bimodal distribution. The mean and median are withal in the heart, just there are two modes: one on each summit.
Other Symmetric Distributions
The normal distribution is the symmetric distribution you're almost likely to meet in uncomplicated statistics. However, at that place are other distributions that display symmetry:
- The bimodal distribution can be symmetrical if the two peaks are mirror images.
- Cauchy distributions have symmetry. You lot're unlikely to come beyond these in elementary stats. They are a family of distributions where the expected value doesn't exist.
- The logistic distribution, which has long tails. The logistic and Cauchy distributions are used if the information is symmetric but in that location are more farthermost values than you lot would wait to detect in a normal distribution. Read more nearly these distribution types hither.
- The uniform distribution is symmetric. The probabilities are exactly the same at each bespeak, so the distribution is basically a directly line. An example of a uniform probability distribution could exist picking a bill of fare from a deck: the probability of picking any one card is the aforementioned: i/52.
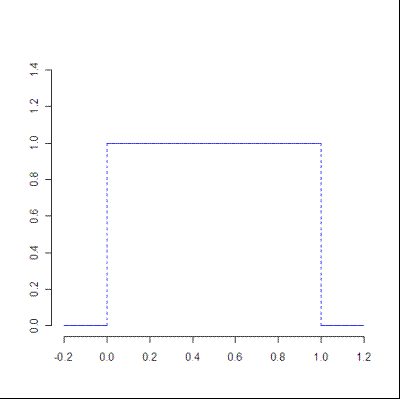
Uniform distribution. Image courtesy of the University of Houston.
References
Fang, K. (2018). Symmetric Multivariate and Related Distributions. Chapman & Hall/CRC.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Need assistance with a homework or test question? With Chegg Study, y'all tin can get step-by-pace solutions to your questions from an adept in the field. Your first thirty minutes with a Chegg tutor is gratuitous!
Comments? Need to post a correction? Please postal service a comment on our Facebook page .
How To Tell If Data Is Symmetric,
Source: https://www.statisticshowto.com/symmetric-distribution-2/
Posted by: nancemaland.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Tell If Data Is Symmetric"
Post a Comment