Which Of The Following Storage Methods Is Used For Storing Long-term Copies Of Organizational Data?
Enterprise information volumes proceed to grow exponentially. So how tin organizations effectively store information technology all? That's where data storage management comes in.
Effective management is key to ensuring organizations utilise storage resources finer, and that they store data securely in compliance with visitor policies and government regulations. IT administrators and managers must sympathize what procedures and tools encompass information storage management to develop their own strategy.
Organizations must keep in mind how storage direction has inverse in recent years. The COVID-19 pandemic increased remote work, the apply of cloud services and cybersecurity concerns such as ransomware. Even before the pandemic, all those elements saw major surges -- and after the pandemic, these elements will still be prominent.
With this guide, explore what data storage management is, who needs it, advantages and challenges, central storage management software features, security and compliance concerns, implementation tips, and vendors and products.
What information storage management is, who needs information technology and how to implement it
Storage management ensures information is available to users when they need it.
Information storage management is typically part of the storage administrator's job. Organizations without a dedicated storage ambassador might use an Information technology generalist for storage direction.
The data memory policy is a key element of storage direction and a skilful starting point for implementation. This policy defines the data an organization retains for operational or compliance needs. It describes why the arrangement must keep the information, the retention period and the procedure of disposal. It helps an organization determine how it can search and access data. The retention policy is especially of import now as data volumes continually increment, and it can assist cut storage space and costs.
The task of information storage management also includes resource provisioning and configuration, unstructured and structured data, and evaluating how needs might change over time.
To help with implementation, a direction tool that meets organizational needs can ease the administrative burden that comes with large amounts of data. Features to wait for in a management tool include storage capacity planning, performance monitoring, compression and deduplication.
Advantages and challenges of data storage management
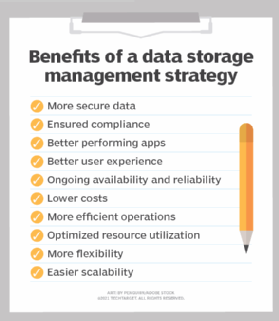
Information storage direction has both advantages and challenges. On the plus side, it improves performance and protects confronting data loss. With effective management, storage systems perform well beyond geographic areas, time and users. It also ensures that information is rubber from exterior threats, human mistake and system failures. Proper backup and disaster recovery are pieces of this data protection strategy.
An effective management strategy provides users with the right amount of storage chapters. Organizations can calibration storage space upwards and down every bit needed. The storage strategy accommodates for constantly irresolute needs and applications.
Storage management also makes it easier on admins past centralizing administration so they tin oversee a diversity of storage systems. These benefits lead to reduced costs as well, every bit admins are able to better utilize storage resource.
Challenges of data storage management include persistent cyberthreats, data management regulations and a distributed workforce. These challenges illustrate why information technology'south and then important to implement a comprehensive plan: A storage management strategy should ensure organizations protect their data against data breaches, ransomware and other malware attacks; lack of compliance could lead to hefty fines; and remote workers must know they'll take access to files and applications but as they would if in a traditional office environs.
Distributed and complex systems present a hurdle for data storage management. Not just are workers spread out, but systems run both on bounds and in the deject. An on-bounds storage environment could include HDDs, SSDs and tapes. Organizations often use multiple clouds. New technologies, such every bit AI, can benefit organizations but besides increment complexity.
Unstructured data -- which includes documents, emails, photos, videos and metadata -- has surged, and this also complicates storage direction. Unstructured data challenges include volume, new types and how to gain value. Although some organizations might non want to spend the fourth dimension to manage unstructured data, in the terminate it saves money and storage infinite. Vendors such as Aparavi, Dell EMC, Pure Storage and Spectra Logic offering tools for this type of direction.
Object storage can provide high performance only also has challenges, including the infrastructure'south scale-out nature and potentially high latency, for example. Organizations must accost problems with metadata performance and cluster management.
Data storage management strategies
Storage management processes and practices vary, depending on the engineering science, platform and type.
Here are some full general methods and services for data storage management:
- storage resource management software
- consolidation of systems
- multiprotocol storage arrays
- storage tiers
- strategic SSD deployment
- hybrid cloud
- scale-out systems
- annal storage of infrequently accessed data
- emptying of inactive virtual machines
- deduplication
- disaster recovery as a service
- object storage
Organizations may consider incorporating standards-based storage management interfaces as office of their management strategy. The Storage Management Initiative Specification and the Intelligent Platform Management Interface are 2 veteran models, while Redfish and Swordfish have emerged equally newer options. Interfaces offer management, monitoring and simplification.
As far as media type, it's tempting to go all-wink considering of its performance. However, to save money, try a hybrid drive choice that incorporates high-capacity HDD and high-speed SSD engineering science.
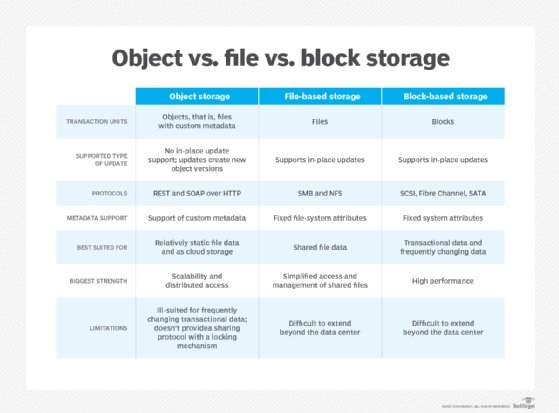
Organizations also must choose among object, block and file storage. Block storage is the default blazon for HDDs and SSDs, and it provides strong performance. File storage places files in folders and offers simplicity. Object storage efficiently organizes unstructured information at a comparatively low toll. NAS is another worthwhile option for storing unstructured data because of its organizational capabilities and speed.
Storage security
With threats both internal and external, storage security is as of import equally ever to a management strategy. Storage security ensures protection and availability past enabling data accessibility for authorized users and protecting against unauthorized admission.
A storage security strategy should have tiers. Security risks are so varied, from ransomware to insider threats, that organizations must protect their data storage in a number of ways. Proper permissions, monitoring and encryption are key to cyberthreat defense.
Offline storage -- for example, in tape backup -- that isn't continued to a network is a stiff way to keep information safe. If attackers can't achieve the data, they tin can't harm it. While information technology's not feasible to keep all data offline, this type of storage is an important aspect of a potent storage security strategy.
Another aspect is off-site storage, one course of which is cloud storage. Organizations shouldn't assume that this keeps their data entirely safe. Users are responsible for their information, and cloud storage is nevertheless online and thus open to some risk.
The surge in remote workers produced a new level of storage security complications, including the following risks:
- less secure dwelling office environments;
- use of personal devices for work;
- misuse of services and applications;
- less formal work habits;
- adjustments to working from home; and
- more opportunities for malicious insiders.
Endpoint security, encryption, access controls and user training aid protect confronting these new storage security issues.
Data storage compliance
Compliance with regulations has e'er been important, but the need has increased in the concluding few years with laws such as the General Information Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act. These laws specifically address information and storage, so information technology's incumbent on organizations to cover them and ensure compliance.
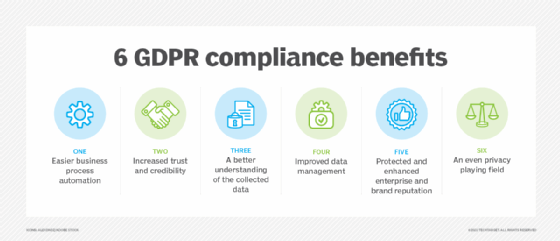
Information storage management helps organizations empathise where they have data, which is a major piece of compliance. Compliance all-time practices include documentation, automation, anonymization and use of governance tools.
Immutable data storage also helps achieve compliance. Immutability ensures retained data -- for example, legal holds -- doesn't change. Vendors such as AWS, Dell EMC and Wasabi provide immutable storage. Nonetheless, organizations should still retain more than 1 re-create of this data, as immutability doesn't protect against physical threats, such equally natural disasters.
Information storage technology, vendors and products
Fundamental features for overall data storage direction providers include resource provisioning, process automation, load balancing, chapters planning and management, predictive analytics, performance monitoring, replication, compression, deduplication, snapshotting and cloning.
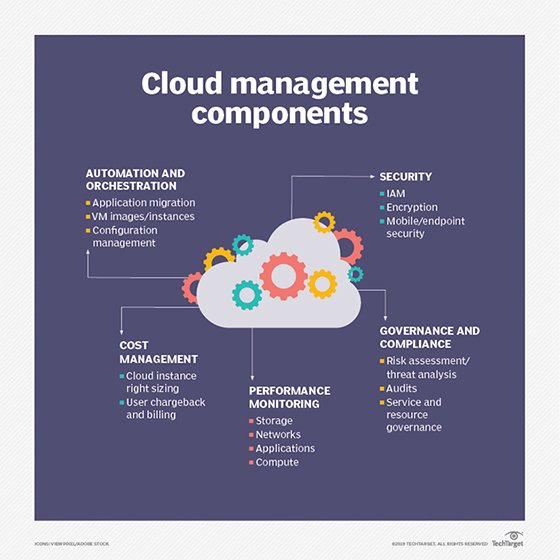
Recent trends amongst vendors include services for cloud storage and the container management platform Kubernetes. Height storage providers tin support a range of different platforms. And though Kubernetes is more than specialized, it has gained traction: Vendors such as Diamanti, NetApp and Pure Storage provide Kubernetes services.
Some course of cloud management is substantially table stakes for storage vendors. A few vendors, including Cohesity and Rubrik, have fabricated cloud data management a hallmark of their platforms. Many organizations use more than than i cloud, so multi-cloud data direction is crucial. Managing data storage across multiple clouds is complex, merely vendors such as Ctera, Dell EMC, NetApp and Nutanix can help.
The time to come of data storage management
Data storage administrators must be fix for a consistently evolving field. Cloud storage was trending up before the pandemic and has skyrocketed since -- and once organizations go to the cloud, they typically stay in that location. Equally a result, admins must understand the various forms of deject storage management, including multi-cloud, hybrid cloud, cloud-native data and cloud information protection.
Hyper-convergence, composable infrastructure and computational storage are too popular frameworks.
In addition, admins must be aware of other new and emerging technologies that help storage management, from automation to machine learning.
Which Of The Following Storage Methods Is Used For Storing Long-term Copies Of Organizational Data?,
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchstorage/Data-storage-management-What-is-it-and-why-is-it-important
Posted by: nancemaland.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Of The Following Storage Methods Is Used For Storing Long-term Copies Of Organizational Data?"
Post a Comment